Beyond Inflammation: Biological Disorder and Biological Harmony
Beyond Inflammation: Biological Disorder and Biological Harmony
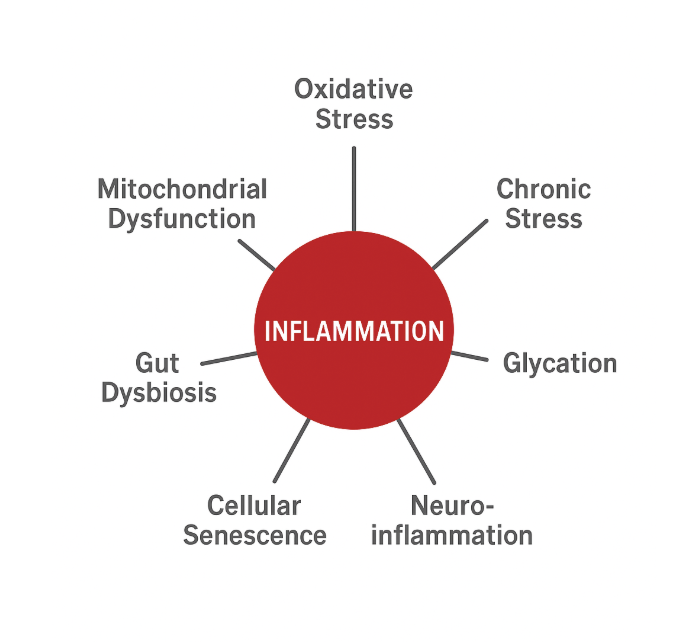
We often focus on inflammation as the primary culprit behind chronic health issues, and for good reason. Inflammation sits at the center of many pathological processes, acting as both a driver and amplifier of dysfunction across systems. But, there are other forces (oxidative stress, chronic stress, glycation, neuroinflammation, cellular senescence, gut dysbiosis, and mitochondrial dysfunction), that feed into inflammation, are amplified by it, or both. This creates a self-reinforcing cycle, where inflammation shapes tissue function, repair, and overall resilience.
Understanding this network of interactions gives us a clearer picture of how health breaks down, and how it can be restored. In this context, we can explore biological disorder and biological harmony: states that reflect how well our systems are coordinated, resilient, and able to repair themselves, with inflammation as the central thread connecting many of these processes.
Below are seven major contributors to biological disorder, with concise explanations and pathways back toward biological harmony:
Inflammation
Oxidative stress, chronic stress, glycation, neuroinflammation, cellular senescence, gut dysbiosis, and mitochondrial dysfunction all strongly influence how balanced or destructive inflammation becomes, determining whether it supports healing or turns harmful.
Oxidative Stress
What it is: An imbalance between free radicals and antioxidants in the body.
How it happens: Poor diet, pollution, excessive UV exposure, and smoking increase free radicals.
Why it matters: Can damage cells, accelerate aging, and cause fatigue.
Disorder: Excess free radicals overwhelm antioxidant defenses, damaging cells, proteins, and DNA.
Harmony: Balanced redox states allow normal signaling and repair, reducing cellular wear-and-tear.
Put Simply: When free radicals overwhelm your system, cells wear down faster, leaving you tired and vulnerable. But when balance is restored, your cells repair smoothly, energy flows, and aging slows.
Chronic Stress
What it is: Long-term activation of the stress response system.
How it happens: Work pressure, emotional strain, and lifestyle imbalance over-activate the stress system.
Why it matters: Disrupts sleep, digestion, immunity, and tissue repair.
Disorder: Persistent stress hormones dysregulate immunity and tissue repair.
Harmony: Restorative balance in the autonomic nervous system supports recovery, adaptability, and resilience.
Put Simply: Living in constant “fight-or-flight” mode disrupts sleep, digestion, and immunity. A calm nervous system restores deep rest, steady energy, and resilience in daily life.
Glycation
What it is: Sugars binding to proteins and lipids, forming harmful end products (AGEs).
How it happens: Driven by excess dietary sugar and processed foods.
Why it matters: Stiffens tissues, affects joints and blood vessels, and accelerates aging.
Disorder: Advanced glycation end products stiffen tissues and accelerate aging.
Harmony: Controlled glucose levels and efficient metabolism maintain tissue flexibility and reduce degenerative changes.
Put Simply: Excess sugar stiffens tissues and accelerates wear-and-tear on joints and vessels. With healthy metabolism, your tissues stay flexible, responsive, and moving with ease.
Neuroinflammation
What it is: Chronic inflammation within the brain and nervous system.
How it happens: Triggered by infection, injury, stress, or poor sleep.
Why it matters: Can cause brain fog, poor coordination, or heightened pain sensitivity.
Disorder: Ongoing immune activation disrupts communication, cognition, and pain regulation.
Harmony: Calming inflammation in neural tissues restores clear signaling and efficient brain-body communication.
Put Simply: Inflammation in the nervous system clouds focus, heightens pain, and slows communication. Clear signaling restores sharp thinking, coordination, and emotional balance.
Cellular Senescence
What it is: Damaged cells that stop dividing but resist dying off.
How it happens: Driven by chronic inflammation, radiation exposure, or repeated injury.
Why it matters: Slows healing and contributes to age-related issues.
Disorder: Senescent cells release inflammatory signals that impair tissue function.
Harmony: Healthy cellular turnover and clearance of senescent cells promote regeneration and tissue vitality.
Put Simply: Damaged cells that won’t retire spread stress and slow healing. Efficient cell turnover keeps tissues youthful, vibrant, and quick to repair.
Gut Dysbiosis
What it is: Imbalance in the gut microbiome ecosystem.
How it happens: Antibiotics, poor diet, stress, or environmental toxins disrupt healthy microbial balance.
Why it matters: Poor gut health can affect digestion, immunity, and mood.
Disorder: Disrupted microbiota produce toxins, weaken the barrier, and amplify systemic inflammation.
Harmony: A diverse, stable microbiome supports digestion, immunity, and systemic regulation.
Put Simply: An unbalanced microbiome can upset digestion, weaken immunity, and even dampen mood. A thriving gut ecosystem supports nutrient absorption, immune strength, and emotional well-being.
Mitochondrial Dysfunction
What it is: Impairment of the cell’s energy-producing organelles.
How it happens: Poor nutrition, chronic stress, environmental toxins, or aging reduce mitochondrial efficiency.
Why it matters: Leads to low energy, slow recovery, and chronic fatigue.
Disorder: Faulty mitochondria lead to fatigue, oxidative damage, and impaired repair.
Harmony: Optimized mitochondrial function sustains cellular energy, resilience, and efficient repair processes.
Put Simply: When mitochondria falter, the body struggles with low energy and repair. When they thrive, energy flows smoothly, supporting vitality and resilience.
TL;DR: Why It Matters
When free radicals overwhelm your system, cells wear down faster, leaving you tired and vulnerable; chronic “fight-or-flight” further disrupts sleep, digestion, and immunity; excess sugar stiffens tissues and accelerates wear-and-tear; inflammation in the nervous system clouds focus and heightens pain; damaged cells that refuse to retire slow healing; an imbalanced gut unsettles digestion, mood, and immunity; and faltering mitochondria drain energy and repair. But when balance is restored across these systems, cells repair smoothly, your nervous system settles, tissues stay flexible, signaling stays clear, turnover remains healthy, the gut thrives, and energy flows with ease—supporting vitality, resilience, and healthy aging.
Balanced inflammation,
stress,
blood sugar,
gut health,
and cellular energy,
are at the heart of feeling vibrant.
Supporting these systems helps your body
repair efficiently,
think clearly,
and sustain energy every day.
How Fascial Counterstrain Supports Biological Harmony
In my practice with Fascial Counterstrain (FCS), a gentle, hands-on technique that releases tension in the fascia and corrects dysfunction throughout nearly every body system, I witness firsthand the transition from disorder toward harmony. FCS works by alleviating restrictions and guarding within the body's fascial network. As fascial tension decreases, circulation and lymphatic flow improve, enhancing the body's capacity to eliminate oxidative byproducts and support various physiological systems.
The nervous system benefits significantly as well: by calming protective reflexes and restoring fascial mobility, FCS helps shift the body away from chronic “fight-or-flight” mode, reducing stress and easing neuroinflammation. Improved tissue mechanics promote nutrient delivery and oxygenation, counteracting stiffness linked to glycation and supporting healthier cellular renewal amid aging.
Within the digestive system, releasing abdominal fascial restrictions enhances motility, blood flow, and communication along the gut-brain axis, contributing to microbiome balance. Overall, FCS does not simply mask symptoms but fosters resilience by creating optimal conditions for regulation, repair, and restoration of harmony across these interconnected systems.
Bringing It Together
These seven forces illustrate how health can unravel into biological disorder, a drift driven by entropy. But they also show us the pathways toward biological harmony, where energy is conserved, communication is clear, and resilience is restored.
Fascial Counterstrain, along with other supportive approaches, offers one way to shift the body away from disorder and back toward harmony. By restoring fascial mobility and reducing systemic strain, FCS can help influence the very processes that drive entropy and disorder.
The takeaway:
Inflammation sits at the center, both shaping and being shaped by other dysfunctions.
Viewing health through the lens of disorder and harmony offers a fuller, actionable understanding, one that acknowledges the forces driving decline, but also the body’s remarkable capacity for self-regulation and renewal.
REFERENCES
-
Jurcău, M. C., et al. (2022).
The Link between Oxidative Stress, Mitochondrial Dysfunction, and Chronic Neuroinflammation. Frontiers in Neuroscience.
Summary – Oxidative Stress & Mitochondria: This review explores how oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction contribute to chronic neuroinflammation, highlighting their roles in neurodegenerative diseases.
🔗 Link -
Baechle, J. J., et al. (2023).
Chronic Inflammation and the Hallmarks of Aging. Ageing Research Reviews.
Summary – Chronic Stress & Aging: The article discusses how chronic stress leads to persistent inflammation, accelerating the aging process and contributing to age-related diseases.
🔗 Link -
Santos, D. F., et al. (2024).
Oxidative Stress and Aging: Synergies for Age-Related Diseases. FEBS Letters.
Summary – Glycation & Tissue Aging: This study examines the interaction between oxidative stress and glycation, emphasizing their combined effect on tissue aging and related diseases.
🔗 Link -
Semenova, N., et al. (2024).
Gut Microbiome Interactions with Oxidative Stress. Antioxidants.
Summary – Neuroinflammation & Cognition: The research highlights how neuroinflammation, influenced by gut microbiome imbalances, affects cognitive functions and overall brain health.
🔗 Link -
Huang, S., et al. (2025).
Global Research Trends in Gut Microbiota and Cellular Senescence. Frontiers in Microbiology.
Summary – Cellular Senescence & Tissue Function: This article reviews the relationship between gut microbiota and cellular senescence, focusing on how microbial imbalances can accelerate aging.
🔗 Link -
Abdolmaleky, H. M., et al. (2024).
Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis, Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Epigenetic Alterations in Metabolic Diseases. Frontiers in Endocrinology.
Summary – Gut Dysbiosis & Metabolic Health: The paper discusses how gut dysbiosis leads to oxidative stress and inflammation, contributing to metabolic diseases through epigenetic changes.
🔗 Link -
Bartman, S. (2024).
Mitochondrial Dysfunction: A Key Player in Brain Aging and Neurodegeneration.
Summary – Mitochondrial Dysfunction & Energy: This review examines the role of mitochondrial dysfunction in brain aging and neurodegenerative diseases, emphasizing its central role in cellular energy production.
🔗 Link -
Tuckey, B. (2021).
Impaired Lymphatic Drainage and Interstitial Inflammatory Stasis in Chronic Musculoskeletal and Idiopathic Pain Syndromes: Exploring a Novel Mechanism. Frontiers in Pain Research.
Summary – Interstitial Inflammatory Stasis: The article proposes that impaired lymphatic drainage leads to interstitial inflammatory stasis, contributing to chronic pain syndromes.
🔗 Link -
Slater, A. M., et al. (2024).
Fascia as a Regulatory System in Health and Disease.
Summary – Fascia Health & Inflammation: The article discusses how fascia functions as a regulatory system in health and disease, highlighting its role in inflammation and tissue repair.
🔗 Link -
Schleip, R., et al. (2022).
Immediate Effects of Myofascial Release Treatment on Lumbar Microcirculation: A Randomized Placebo-Controlled Trial.
Summary – Fascia & Circulation: This study investigates the immediate effects of myofascial release treatment on lumbar microcirculation, providing insights into the therapeutic potential of fascia-targeted interventions.
🔗 Link -
Xu, X., et al. (2025).
Mitochondria in Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Aging: From Mechanisms to Therapeutic Advances.
Summary – Mitochondrial Health & Systemic Wellness: This comprehensive review discusses how mitochondrial dysfunction serves as a central hub linking oxidative stress, inflammation, and aging, contributing to various diseases and overall wellness.
🔗 Link